本文最后更新于 2024年7月18日 晚上
最难受的一集。
模型
Assimp
3D建模工具如Blender、3DS Max在导出模型文件时,会自动生成所有的顶点坐标、顶点法线和纹理坐标。
.obj格式只包含了模型数据和材质信息(颜色、贴图等),而collada格式则非常丰富,甚至包含了场景、摄像机信息等。
Assimp是一个开源的模型导入库,支持数十种不同的3D模型格式。
使用Assimp导入模型时,通常会把模型加载入一个场景(Scene)对象,它包含了导入的模型/场景内的所有数据。Assimp会把场景载入为一系列的节点,每个节点包含了场景对象中存储数据的索引。
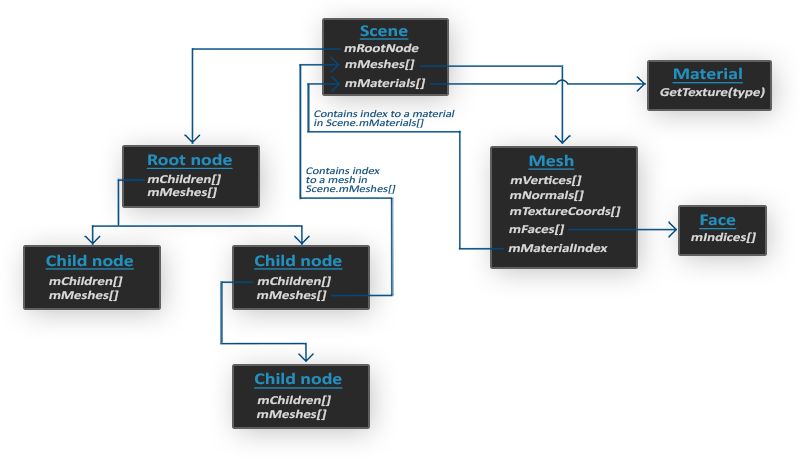
Scene节点包含了对场景根节点的引用。根节点包含的子节点会有一系列指向场景节点中mMeshes数据中存储的网格数据的索引。Scene节点的mMeshes数组存储了真正的Mesh对象。
我们可以这么理解:真正的Mesh数据存在Scene节点里,Scene节点本身在层级面板中不可见;
根节点和子节点就像是层级面板中的父对象和一个个子对象,它们不存储数据,只存储索引。
Mesh对象包含了渲染需要的所有数据,如顶点位置、法向量、纹理坐标、面(Face)和材质(含贴图等)。
面指的是物体的渲染图元(Primitive),如三角形、点、线等。面包含了组成图元的顶点和索引。
借助Assimp加载模型的步骤如下:
- 加载物体到Scene对象中
- 遍历所有节点,获取每个节点对应的Mesh对象
- 处理每个Mesh对象以获取渲染所需的数据
完成上述步骤后,我们得到的是一系列Mesh数据,被包含在一个Model对象中。
一个Model由若干个Mesh组成。一个Mesh是一个单独的形状,是OpenGL里绘制物体的最小单位。
引入工程
在Github Release页面下载最新版本的Assimp源码:assimp/assimp: The official Open-Asset-Importer-Library Repository. Loads 40+ 3D-file-formats into one unified and clean data structure. (github.com)
把根目录在Clion中打开,然后构建项目,把构建好的dll放到libs文件夹下,随后修改CMakeList.txt:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.28)
project(LearnOpenGL)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_DEBUG "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_DEBUG} -O0 -g")
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)
set(GLFW_INCLUDE_DIR "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include/GLFW")
set(GLFW_LIB_DIR "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/libs")
set(GLFW_LIBRARY "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/libs/glfw3.dll")
set(ASSIMP_LIBRARY "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/libs/libassimp-5d.dll")
set(ASSIMP_INCLUDE_DIR "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include/assimp")
add_library(IMGUI SHARED
./imgui/imgui.cpp
./imgui/imgui_impl_glfw.cpp
./imgui/imgui_impl_opengl3.cpp
./imgui/imgui_draw.cpp
./imgui/imgui_tables.cpp
./imgui/imgui_widgets.cpp
./imgui/imgui_demo.cpp
./imgui/imgui_stdlib.cpp
)
target_link_libraries(IMGUI PRIVATE ${GLFW_LIBRARY})
add_executable(LearnOpenGL
Archive/main.cpp
glad.c
include/shader_s.h
GLMTest.cpp
stbitmp.cpp
include/camera.h
include/mesh.h
include/model.h
include/shader.h
)
include_directories(${GLFW_INCLUDE_DIR} "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include" ${ASSIMP_INCLUDE_DIR})
target_link_libraries(LearnOpenGL PRIVATE ${GLFW_LIBRARY} IMGUI ${ASSIMP_LIBRARY})
|
Assimp数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| struct aiNode{
aiNode **mChildren;
unsigned int *mMeshes;
aiMetadata* mMetaData;
aiString mName;
unsigned int mNumChildren;
unsigned int mNumMeshes;
aiNode *mParent;
aiMatrix4x4 mTransformation;
}
struct aiScene{
aiAnimation** Animations;
aiCamera** mCameras;
unsigned int mFlags;
aiLight** mLights;
aiMaterial** mMaterials;
aiMesh** mMeshes;
aiMetadata* mMetaData;
aiString mName;
unsigned int mNumAnimations;
unsigned int mNumCameras;
unsigned int mNumLights;
unsigned int mNumMaterials;
unsigned int mNumMeshes;
unsigned int mNumTextures;
aiNode* mRootNode;
aiTexture **mTextures;
}
struct aiMesh{
aiAnimMesh** mAnimMeshes;
aiVector3D* mBitangents;
aiBone** mBones;
aiColor4D* mColors[AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_COLOR_SETS];
aiFaces* mFaces;
unsigned int mMaterialIndex;
unsigned int mMethod;
aiString mName;
aiVector3D* mNormals;
unsigned int mNumAnimMeshes;
unsigned int mNumBones;
unsigned int mNumFaces;
unsigned int mNumUVComponents[AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_TEXTURECOORDS];
unsigned int mNumVertices;
unsigned int mPrimitiveTypes;
aiVector3D* mTangents;
aiVector3D* mTextureCoords[AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_TEXTURECOORDS];
aiString mTextureCoordsNames[AI_MAX_NUMBER_OF_TEXTURECOORDS];
aiVector3D* mVertices;
}
|
网格
网格(Mesh)代表的是单个可绘制实体,它包含了顶点数据、索引和纹理数据。
我们来逐个考虑需要的属性:
- 顶点由一个位置向量定义,为了让顶点表现出正常的光照效果,我们需要定义顶点的法向量。同时,纹理坐标使得纹理能正确映射到形状表面。这三个属性恰好是我们之前在VBO中存储的数据。
- 纹理对象生成后由一个无符号整数句柄引用。同时,为了知道这个纹理是漫反射贴图、高光贴图还是别的什么,我们需要一个字符串(或枚举)来定义它的类型。
由此定义结构体:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| struct Vertex {
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Normal;
glm::vec2 TexCoords;
}
struct Texture{
unsigned int id;
string type;
aiString path;
}
|
由于索引只是无符号整数的几何,所以无需单独定义结构体。
定义完网格对象中存储的内容后,就可以着手构建网格类了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class Mesh{
public:
vector<Vertex> vertices;
vector<unsigned int> indices;
vector<Texture> textures;
Mesh(vector<Vertex> vertices, vector<unsigned int> indices, vector<Texture> textures);
void Draw(Shader shader);
private:
vector<Texture> textures_loaded;
unsigned int VAO,VBO,EBO;
void setupMesh();
}
|
初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| Mesh(vector<Vertex> vertices, vector<unsigned int> indices, vector<Texture> textures){
this.vertices = vertices;
this.indices = indices;
this.textures = textures;
setupMesh();
}
void setupMesh(){
glGenVertexArrays(1,&VAO);
glGenBufferArrays(1,&VBO);
glGenBufferArrays(1,&EBO);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices.size()*sizeof(Vertex), &vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices.size()*sizeof(unsigned int), &indices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)offsetof(Vertex, Normal));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)offsetof(Vertex, TexCoords));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
glBindVertexArray(0);
}
|
注意:offsetof(struct attrib)关键字可以用于求取属性attrib在结构体struct内的偏移值(字节单位)。但由于结构体内的属性在内存上是连续的,所以实际上也可以用x * sizeof(float)来代替。
渲染
Draw函数用于设置uniform,指定绘制操作等。
我们定义:着色器中采样器的名称应当被定义为texture_diffuseN、texture_specularN,其中N∈[1, MAX_TEXTURE_COUNT]。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| void Draw(Shader &shader) {
unsigned int diffuseNr = 1;
unsigned int specularNr = 1;
for(unsigned int i=0;i<(int)textures.size();i++) {
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0+i);
string name = textures[i].type;
string number;
if(name=="texture_diffuse") {
number = std::to_string(diffuseNr++);
}
else if(name=="texture_specular") {
number = std::to_string(specularNr++);
}
shader.setInt(("material."+name+number).c_str(),i);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D,textures[i].id);
}
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES,(sizeof(unsigned int))*(int)indices.size(),GL_UNSIGNED_INT,0);
glBindVertexArray(0);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
}
|
导入模型
前面我们了解到,一个Model对象包含多个Mesh对象。据此,我们定义Model类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| class Model{
public:
Model(char *path){
loadModel(path);
}
void Draw(Shader shader);
private:
vector<Mesh> meshes;
string directory;
void loadModel(string path);
void processNode(aiNode *node, const aiScene *scene);
Mesh processMesh(aiMesh *mesh, const aiScene *scene);
vector<Texture> loadMaterialTextures(aiMaterial *mat, aiTextureType type, string typeName);
}
|
对于Draw函数,遍历所有的网格,并调用它们的Draw函数。
1
2
3
4
5
| void Draw(Shader shader){
for(unsigned int i=0;i<(int)meshes.size();i++){
meshes[i].Draw(shader);
}
}
|
对于使用Assimp相关代码的源文件,需要包含Importer.hpp、scene.h以及postprocess.h头文件。
Importer类用于快速地加载模型文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| void loadModel(string path){
Assimp::Importer importer;
const aiScene *scene = importer.ReadFile(path, aiProcess_Triangulate | aiProcess_FlipUVs);
if(!scene||scene->mFlags&AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE||!scene->mRootNode){
cout<<"ERROR::ASSIMP::"<<import.GetErrorString()<<endl;
return;
}
directory = path.substr(0,path.find_last_of('/'));
processNode(scene->mRootNode,scene);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| void processNode(aiNode *node, const aiScene* scene){
for(unsigned int i=0;i<node->mNumMeshes;i++){
aiMesh *mesh = scene->mMeshes[node->mMeshes[i]];
meshes.push_back(processMesh(mesh,scene));
}
for(unsigned int i=0;i<node->mNumChildren;i++){
processNode(node->mChildren[i],scene);
}
}
|
之所以费这么多心思遍历子节点获取网格,而不是直接遍历aiScene的Mesh数组,是因为:
无论是在游戏引擎里还是在3D建模软件中,都存在类似层级面板的东西。在这里,网格之间有严格的父子关系,而节点之间的关系就体现了这一点。
如果单纯遍历Mesh数组,那网格之间的父子关系就被丢弃了。
processMesh函数用于把aiMesh对象转换为我们自己的Mesh类。实现这一步很简单,只需要访问aiMesh的所有属性,并把它们赋值给Mesh类的属性即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| Mesh processMesh(aiMesh* mesh, const aiScene* scene){
vector<Vertex> vertices;
vector<Texture> textures;
vector<unsigned int> indices;
for(unsigned int i=0;i<mesh->mNumVertices;i++){
Vertex vertex;
glm::vec3 tmpVec;
tmpVec.x = mesh->mVertices[i].x;
tmpVec.y = mesh->mVertices[i].y;
tmpVec.z = mesh->mVertices[i].z;
vertex.Position = tmpVec;
tmpVec.x = mesh->mNormals[i].x;
tmpVec.y = mesh->mNormals[i].y;
tmpVec.z = mesh->mNormals[i].z;
vertex.Normal = tmpVec;
glm::vec2 uv;
if(mesh->mTexCoords[0]){
uv.x = mesh->mTexCoords[0][i].x;
uv.y = mesh->mTexCoords[0][i].y;
vertex.TexCoords = uv;
}
else{
vertex.TexCoords = glm::vec2(0.0f,0.0f);
}
vertices.push_back(vertex);
}
for(unsigned int i=0;i<mesh->mNumFaces;i++){
aiFace face = mesh->mFaces[i];
for(unsigned int j=0;j<face.mNumIndices;j++){
indices.push_back(face.mIndices[j]);
}
}
if(mesh->mMaterialIndex>=0){
aiMaterial *material = scene->mMaterials[mesh->mMaterialIndex];
vector<Texture> diffuseMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material,aiTextureType_DIFFUSE,"texture_diffuse");
textures.insert(textures.end(),diffuseMaps.begin(),diffuseMaps.end());
vector<Texture> specularMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material,aiTextureType_SPECULAR,"texture_specular");
textures.insert(textures.end(),specularMaps.begin(),specularMaps.end());
}
}
|
到这里,我们Mesh类的属性就都填充完毕了。接下来,我们要结合stbi_image库来加载材质中的纹理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| vector<Texture> loadMaterialTextures(aiMaterial* mat, aiTextureType type, string typeName){
vector<Texture> textures;
for(unsigned int i=0;i<mat->GetTextureCount(type);i++){
aiString str;
mat->GetTexture(type,i,&str);
bool skip = false;
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < this->textures_loaded.size(); j++)
{
if(std::strcmp(textures_loaded[j].path.data(), str.C_Str()) == 0)
{
textures.push_back(textures_loaded[j]);
skip = true;
break;
}
}
if(!skip){
Texture texture;
texture.id = TextureFromFile(str.C_Str(),this->directory);
texture.type = typeName;
texture.path = str;
textures.push_back(texture);
}
}
return textures;
}
unsigned int TextureFromFile(const char* path, const string &directory){
string filename = string(path);
filename = directory + '/' + filename;
unsigned int id;
glGenTextures(1,&id);
int width, height, channels;
unsigned char* data = stbi_load(filename.c_str(), &width,&height,&channels,0);
if(data){
GLenum format;
if(channels==1){
format = GL_RED;
}
else if(channels==3){
format = GL_RGB;
}
else if(channels==4){
format = GL_RGBA;
}
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D,id);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, format, width, height, 0, format, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
stbi_image_free(data);
}
else{
std::cout << "Texture failed to load at path: " << path << std::endl;
stbi_image_free(data);
}
return id;
}
|
记得修改Shader:
1
2
3
4
5
| struct Material{
sampler2D texture_diffuse1;
sampler2D texture_specular1;
float shininess;
};
|
